Introduction to Cross-Chain Bridges and Platform Solutions
In the blockchain ecosystem, interoperability has become increasingly crucial as various blockchain networks operate independently, each with its own protocols, consensus mechanisms, and use cases. The need for communication between these networks has led to the development of Cross-Chain Bridges and other blockchain development solutions. This article will explore the concept of Cross-Chain Bridges, their significance, and how they enable cross-chain compatibility in the blockchain space.
What are Cross-Chain Bridges?
Cross-Chain Bridges are specialized protocols designed to facilitate communication and transfer of assets or data between two or more different blockchain networks. Blockchains like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana operate independently, each with its unique architecture. However, users and developers often need to interact across multiple networks, which is where Cross-Chain Bridges play a pivotal role.
By utilizing Cross-Chain Bridges, users can seamlessly transfer tokens, NFTs, or other digital assets from one blockchain to another without relying on centralized exchanges or custodians. These bridges ensure that assets maintain their value and function when they move between chains, making decentralized applications (dApps) more versatile and interoperable.
The Importance of Cross-Chain Compatibility
At the core of blockchain technology growth is the need for cross-chain compatibility. This concept refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and share information or assets. Without cross-chain compatibility, blockchain ecosystems would remain siloed, limiting their potential and hindering innovation. By fostering connectivity, Cross-Chain Bridges enable a more integrated and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
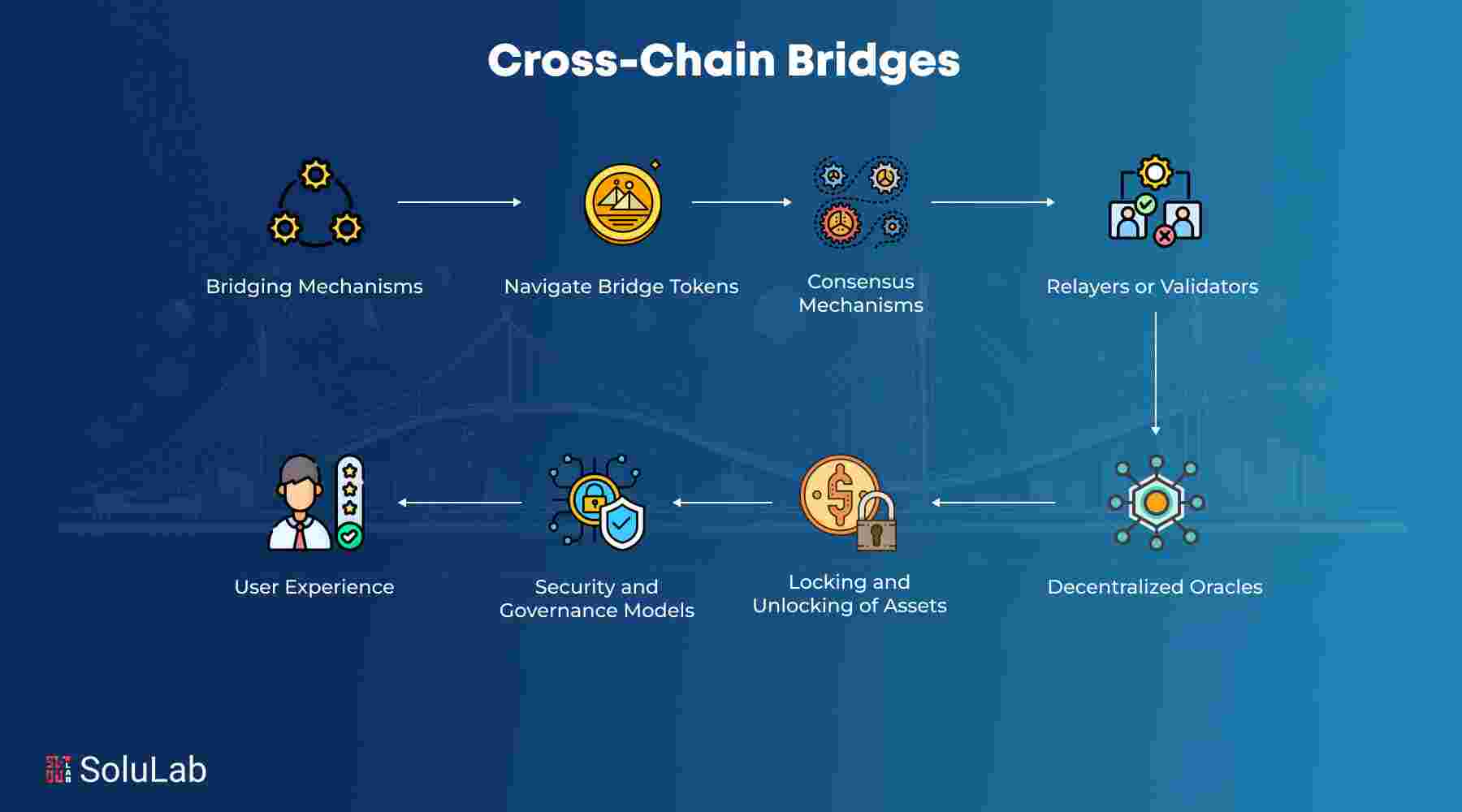
How Cross-Chain Bridges Work
Cross-Chain Bridges typically use a mechanism that locks assets on the originating chain and mints an equivalent asset on the target chain. When users want to transfer tokens from one chain to another, the bridge locks the original tokens in a smart contract on the first blockchain, and an equivalent number of tokens are issued on the second blockchain.
Key technologies that power these bridges include:
- Lock-and-mint mechanisms: Assets are locked on one chain, and a new, corresponding asset is minted on the destination chain.
- Validators and oracles: These entities verify transactions between chains, ensuring the integrity of the transfer.
- Atomic swaps: A decentralized exchange mechanism that allows the direct trade of tokens across different chains without intermediaries.
Blockchain Development Solutions for Cross-Chain Bridges
Creating Cross-Chain Bridges requires advanced blockchain development solutions. These solutions are designed to overcome the inherent limitations of isolated blockchain networks, ensuring that transactions and data transfers are secure, efficient, and transparent.
Developers working on Cross-Chain Bridges need to address several challenges, such as:
- Security risks: Since bridges interact with multiple chains, they can become attractive targets for attacks. Secure blockchain development solutions are necessary to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure the safe transfer of assets.
- Scalability: Bridges must handle high transaction volumes while maintaining fast and efficient transfers. This requires innovative solutions for optimizing performance across chains.
- Decentralization: Some Cross-Chain Bridges are controlled by centralized entities, which can limit their decentralized nature. Emerging solutions focus on creating fully decentralized bridges that operate without intermediaries.
Popular Cross-Chain Bridge Platforms
Several platforms have emerged as leaders in the development of Cross-Chain Bridges. These platforms provide the infrastructure and tools needed to enable cross-chain compatibility across a wide range of blockchain networks.
- Polkadot: Polkadot is a multi-chain network that facilitates communication between different blockchains through its parachain model. Polkadot’s design allows for seamless cross-chain compatibility and asset transfers, making it a popular choice for developers building decentralized applications that need to interact across chains.
- Cosmos: Known as the "internet of blockchains," Cosmos provides a robust infrastructure for building interoperable blockchain networks. Its Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol allows different blockchains to communicate and transfer assets, creating a truly interconnected ecosystem.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC) Bridge: Binance Smart Chain offers its own Cross-Chain Bridge, allowing users to transfer assets between BSC and other blockchain networks like Ethereum. The BSC bridge is one of the most widely used in the DeFi space due to its fast transaction speeds and low fees.
The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the need for Cross-Chain Bridges and cross-chain compatibility will only grow. More decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, and supply chain applications will require seamless movement of assets and data across different blockchains. This will fuel the demand for innovative blockchain development solutions that focus on enhancing security, scalability, and ease of use.
Moreover, as more blockchain platforms adopt multi-chain frameworks and integrate Cross-Chain Bridges, users will benefit from a more interconnected and flexible ecosystem. This will lead to a future where the barriers between blockchain networks are minimized, allowing for a unified and efficient decentralized world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Cross-Chain Bridges are an essential component of the blockchain landscape, enabling cross-chain compatibility and fostering a more interconnected ecosystem. Through advanced blockchain development solutions, these bridges ensure secure, scalable, and efficient asset transfers between different blockchain networks. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the importance of Cross-Chain Bridges will only increase, making them a fundamental building block for the future of decentralized applications and services.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


