Zero Liquid Discharge Systems Market Driving Factors, Investment Feasibility, and Analysis by 2032
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems are an advanced water treatment technology designed to ensure that no liquid waste is discharged into the environment. These systems are highly efficient at treating wastewater by recovering nearly all the water, which can then be reused, while solid waste is minimized. ZLD systems integrate various technologies such as reverse osmosis (RO), evaporation, crystallization, and filtration, which allow for the treatment and recovery of both water and salts or other minerals. The treated water can be reused for industrial processes, irrigation, or even potable applications, depending on the level of treatment. This process not only minimizes the environmental impact of industrial wastewater but also helps in conserving water, which is becoming an increasingly scarce resource in many parts of the world. ZLD systems are commonly employed in industries such as power generation, textiles, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where high volumes of wastewater are generated and the demand for water reuse is critical. With growing regulatory pressure on wastewater discharge and increasing concerns about water scarcity, ZLD systems have emerged as an essential solution for industries aiming to reduce their environmental footprint and improve resource efficiency.
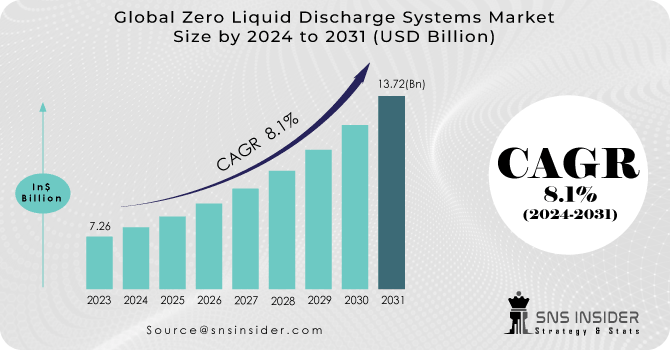
The Zero Liquid Discharge Systems Market size was valued at USD 7.26 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to USD 13.72 billion by 2031 and grow at a CAGR of 8.1% over the forecast period of 2024-2031.
Future Scope
The future scope of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems is promising, particularly as water scarcity becomes a more pressing issue worldwide and environmental regulations become more stringent. As industries continue to face challenges related to wastewater treatment and disposal, ZLD systems provide a sustainable solution by minimizing liquid discharge and enabling water reuse. The rising global demand for water conservation and sustainability will drive the widespread adoption of ZLD technologies across multiple sectors, including power generation, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. With advancements in filtration and membrane technology, as well as improvements in energy efficiency, ZLD systems are expected to become more cost-effective and accessible to a broader range of industries. Additionally, the development of more compact, modular, and scalable systems will make ZLD solutions viable for smaller operations and regions with limited infrastructure. Governments and regulatory bodies are also likely to increase the pressure on industries to adopt ZLD systems as part of their environmental compliance strategies, further accelerating the growth of this market. Furthermore, as companies and industries move toward circular economy models, the emphasis on resource recovery and closed-loop systems will provide new opportunities for the expansion of ZLD technologies.
Emerging Trends
Several key trends are shaping the Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) market, reflecting the growing emphasis on sustainability and resource conservation. One of the most prominent trends is the increasing adoption of ZLD in industries with significant water consumption, such as power plants, oil and gas operations, and textile manufacturing. These industries generate large volumes of wastewater, and ZLD systems offer a sustainable solution to manage their effluent while conserving water for reuse. Another emerging trend is the development of more energy-efficient and cost-effective ZLD technologies. Innovations in membrane filtration, reverse osmosis, and crystallization processes are making ZLD systems more affordable and efficient, addressing one of the main challenges associated with their widespread implementation—high operational and energy costs. The integration of ZLD systems with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, is also gaining traction, as it helps reduce the carbon footprint of water treatment operations. Additionally, digitalization and automation are becoming more prevalent in ZLD systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and optimization of water recovery processes, improving efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. The trend toward water reuse and resource recovery is expanding, with industries looking to implement closed-loop systems where treated water is not only reused but also converted into valuable byproducts such as salts, chemicals, or energy.
Drivers
The primary drivers for the growth of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems include increasing water scarcity, stringent environmental regulations, and growing demand for sustainable industrial practices. As fresh water becomes increasingly scarce in many regions, industries are under pressure to reduce their reliance on municipal water supplies and recycle their wastewater. ZLD systems provide an effective solution by enabling water reuse, reducing the need for fresh water intake, and minimizing environmental impact. Regulatory bodies are also playing a significant role in driving the adoption of ZLD technologies, as many regions have enacted or are in the process of implementing stricter regulations on wastewater discharge. Companies that adopt ZLD systems can avoid costly fines and penalties associated with non-compliance, while also enhancing their environmental credentials. Additionally, the growing focus on sustainability and resource conservation is motivating industries to adopt ZLD systems as part of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) strategies. The desire to achieve a circular economy, where water and other resources are continually recycled and reused, is further accelerating the demand for ZLD technologies. In sectors such as power generation, textiles, and food processing, ZLD offers a solution to reduce waste and improve operational efficiency, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to improve their sustainability profiles.
Restraints
While the Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) market has significant growth potential, there are several restraints that could impact its widespread adoption. One of the key challenges is the high initial investment and operational costs associated with ZLD systems. The advanced technology and infrastructure required for wastewater treatment, along with energy-intensive processes such as evaporation and reverse osmosis, can make ZLD systems expensive to implement and maintain, particularly for smaller industries. Additionally, the complexity of designing and integrating ZLD systems into existing industrial processes can be a barrier for companies looking to adopt this technology. The disposal of residual waste, such as salts and chemicals recovered during the ZLD process, can also pose challenges, as these byproducts need to be handled and disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner. Another restraint is the energy consumption of certain ZLD technologies, which can be a significant operational cost. While innovations in energy efficiency are helping to address this issue, the high energy requirements of some ZLD processes remain a concern. Furthermore, the lack of proper infrastructure and technical expertise in some regions could limit the adoption of ZLD systems, particularly in developing countries where water treatment facilities may be lacking.
Key Points
· Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems are designed to eliminate liquid waste discharge by recovering water and minimizing environmental impact, offering a sustainable solution for wastewater treatment.
· ZLD systems are gaining traction across industries such as power generation, textiles, chemicals, and food processing, where water conservation and regulatory compliance are critical.
· Emerging trends include the development of energy-efficient and cost-effective technologies, integration with renewable energy sources, and the growing trend of digitalization and automation in ZLD systems.
· Key drivers include increasing water scarcity, stringent regulations on wastewater discharge, and the rising demand for sustainable and circular economy practices.
· Restraints include high initial investment and operational costs, energy consumption, challenges related to residual waste disposal, and the complexity of integrating ZLD systems into existing operations.
The market for Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems is set to expand as industries and governments focus on sustainability and water conservation. With continued innovation in technology and greater regulatory pressure, ZLD systems are becoming an essential part of the solution for industries seeking to minimize environmental impact while optimizing resource use.
Get Free Sample Copy @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/2826
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


